GIGEIIN > Conservation of Cultural Property Department


GIGEIIN > Conservation of Cultural Property Department
As mentioned in the introduction to GIGEIIN, the Faculty of Arts and Design of the University of Toyama has a history of contributing to the development of local craft culture through education and research. It has been working with the national government for over 15 years, including Takaoka Mikurumayama. We have been involved in the conservation and restoration of important designated tangible and intangible folk cultural properties. As a group of researchers specializing in metal crafts, wood crafts, lacquer crafts, architectural structures, and cultural policy, we refine conventional manual techniques through research and production of works, and education. Several years ago, we started using digital techniques such as 3D scanners. We use equipment to collect data on the objects to be repaired. We use this data to discuss and verify the repair work and create jigs and templates for use in the work. Recently, we added staff members specializing in digital technology. We are now capable of generating 3D images by overlaying colors and textures from photographic data while simultaneously collecting 3D data of the repair target. This enables the generation of high-quality digital archives. This is one of my goals. Research and analysis from a scientific perspective is essential when restoring cultural properties. Component analysis is now feasible using a fluorescent X-ray analyzer. We also utilize our strengths as a comprehensive university to conduct research in collaboration with the Faculty of Engineering and
the School of Medicine. We have demonstrated achievements in research. In addition, we would collaborate with highly skilled craft engineers in the Hokuriku region
and cultural property managers of related local governments to achieve more precise and high-quality cultural property preservation for the future. This is also aimed at the development of the next generation. We aim to develop a system that would endure.
When addressing cultural properties, we consider it important 1) to have a wide range of knowledge and high-level skills to perform accurate repairs and 2) to be capable of responding with humility while understanding the various backgrounds of each cultural property.
The Noto Peninsula Earthquake that occurred on January 1, 2024 caused severe damage to the entire Noto Peninsula. We should design and implement measures to support those affected by the disaster and to rebuild the region. The GIGEIIN intends to actively collaborate with activities aimed at revitalizing the local culture.
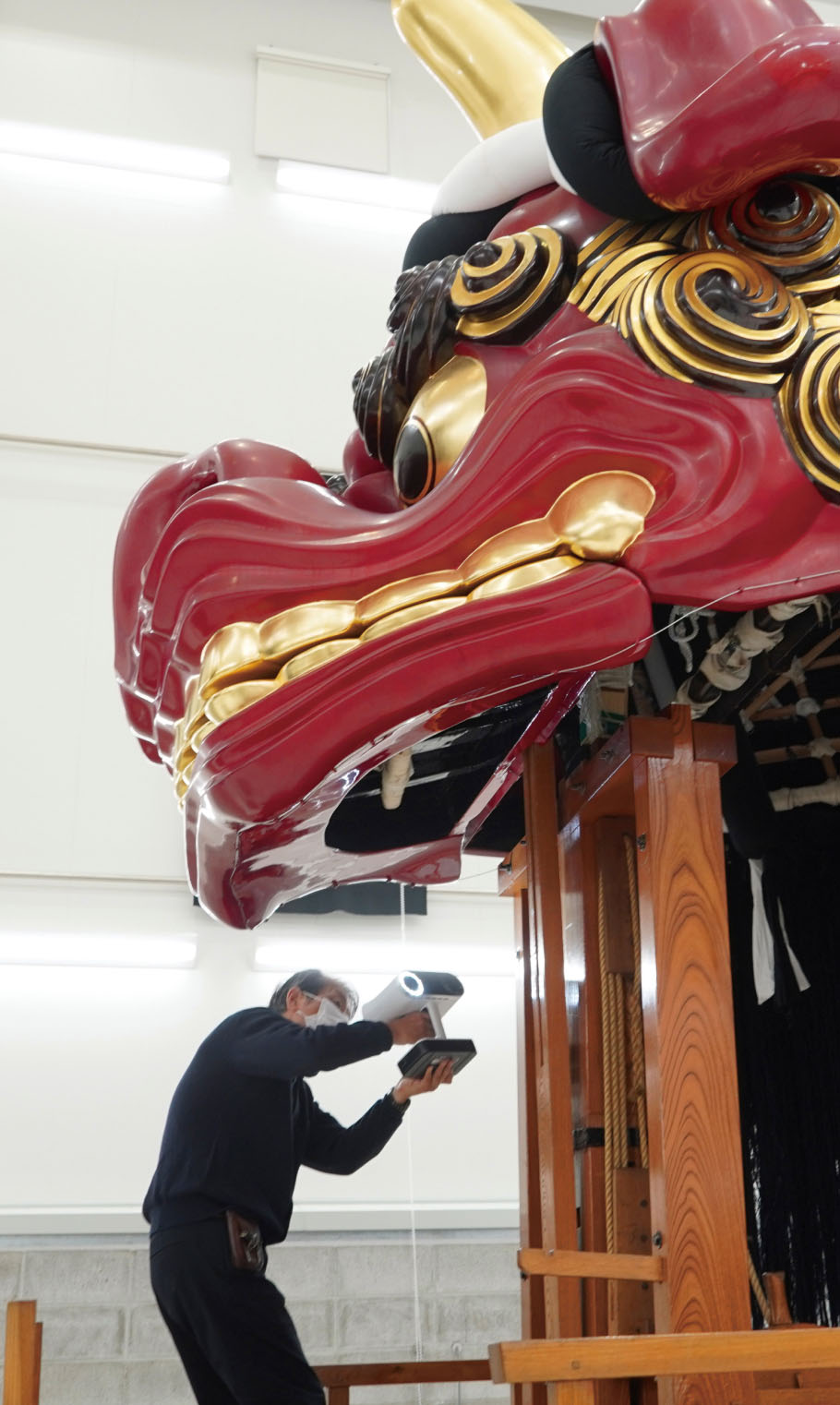

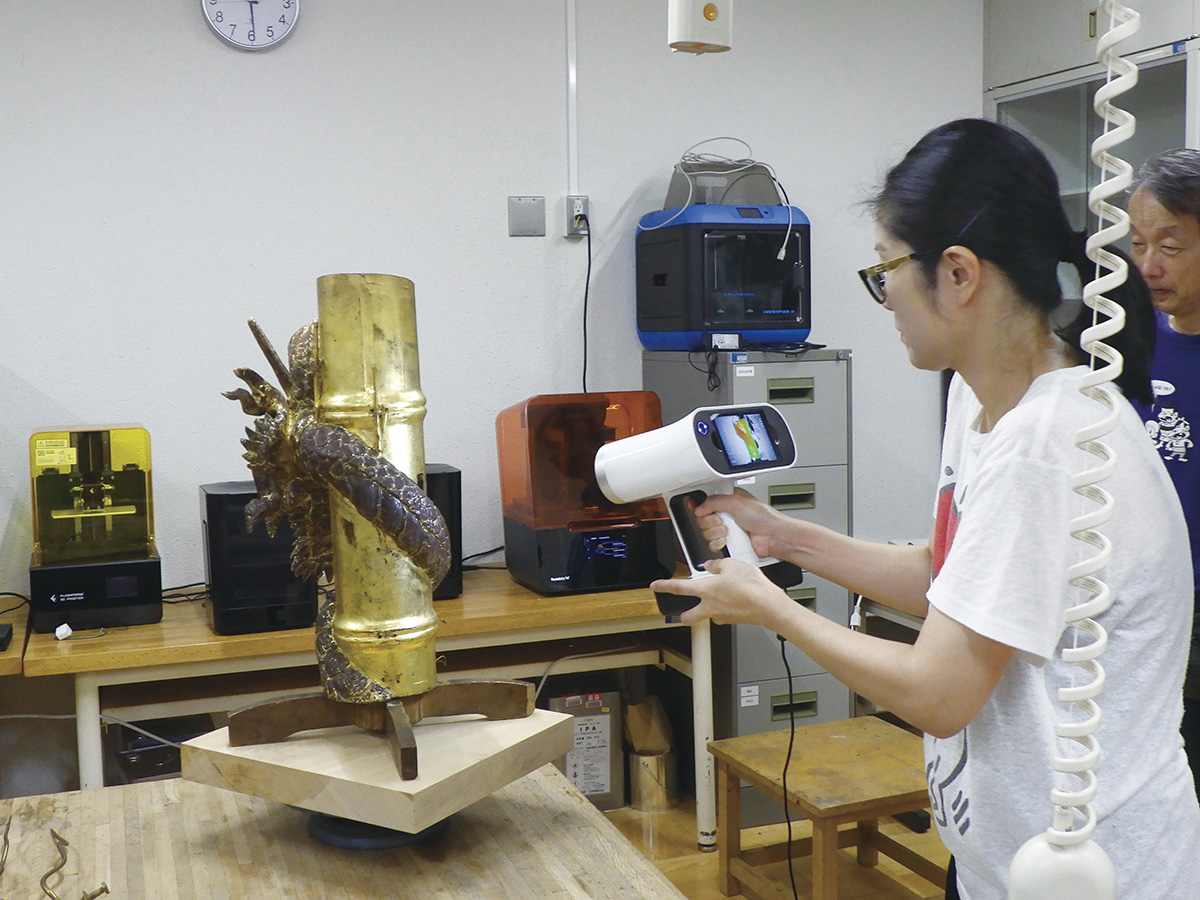
3D scan for making a precise model of the Karatsu-kunchi “Ichibanzan AkaJishi” a nationally-designated Important Intangible Folk Cultural Property
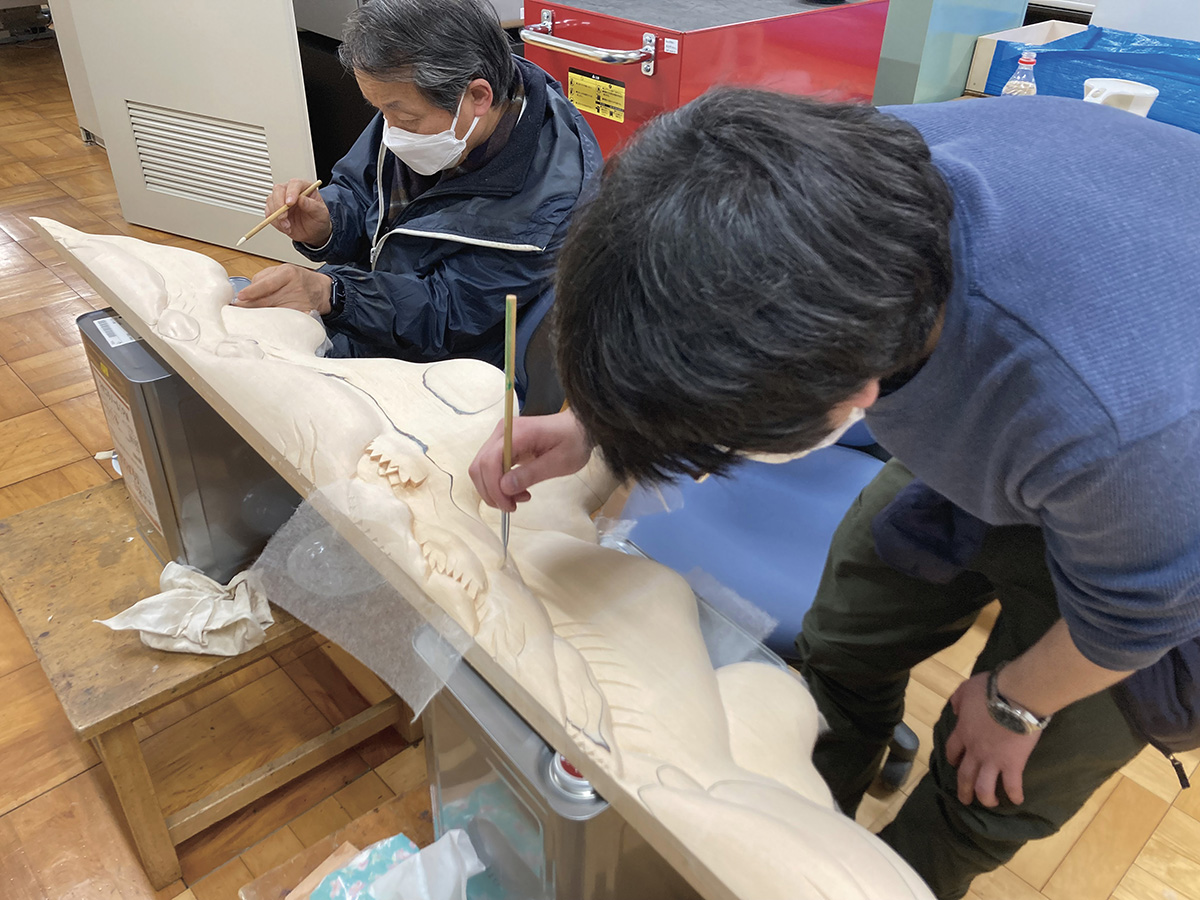

Washi application process before the Gofun coloring of “Yukiyama”, a decorative parts in Takaoka Mikurumayama.
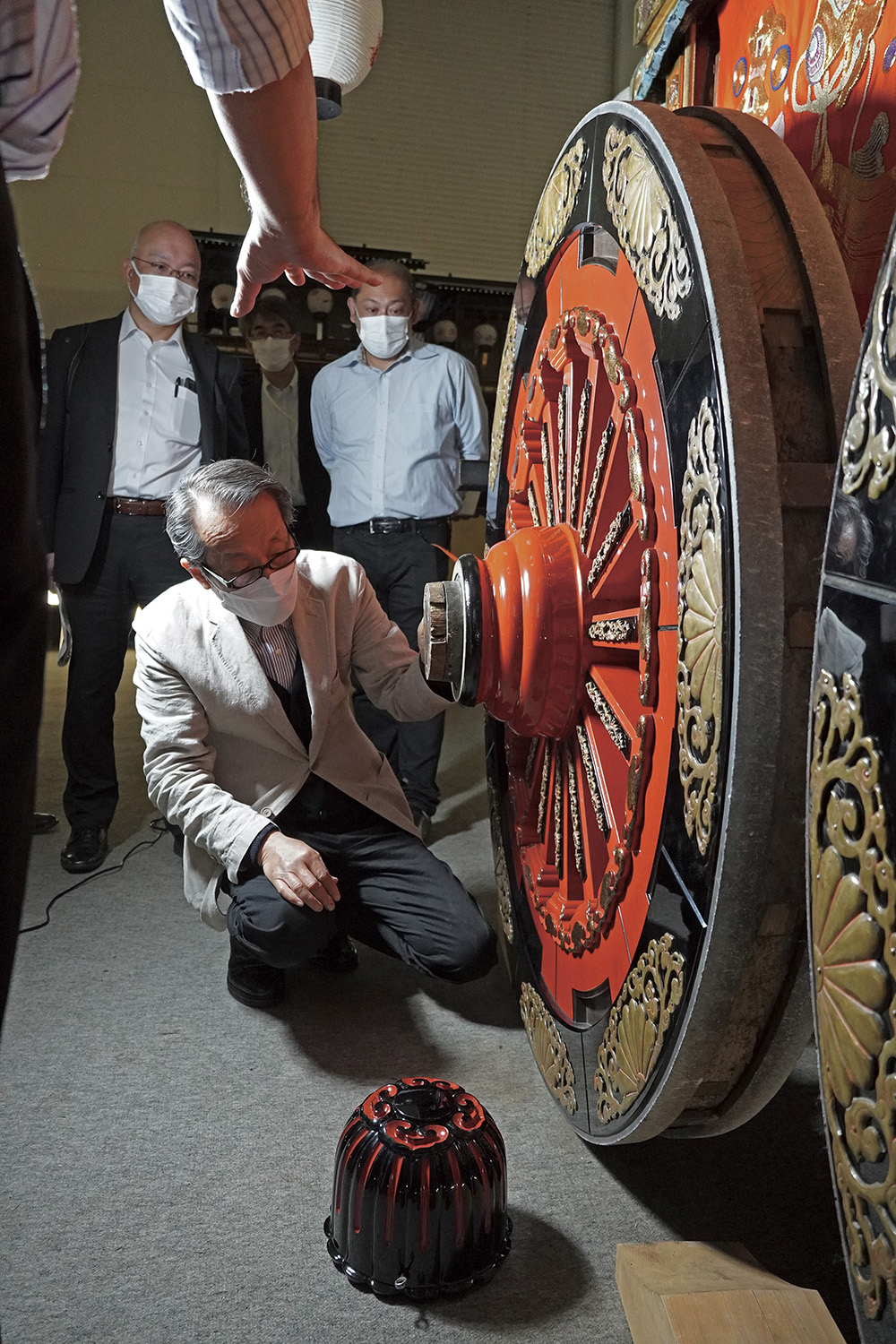

Investigation of wheel repair for floats at the Jyohana Hikiyama Festival
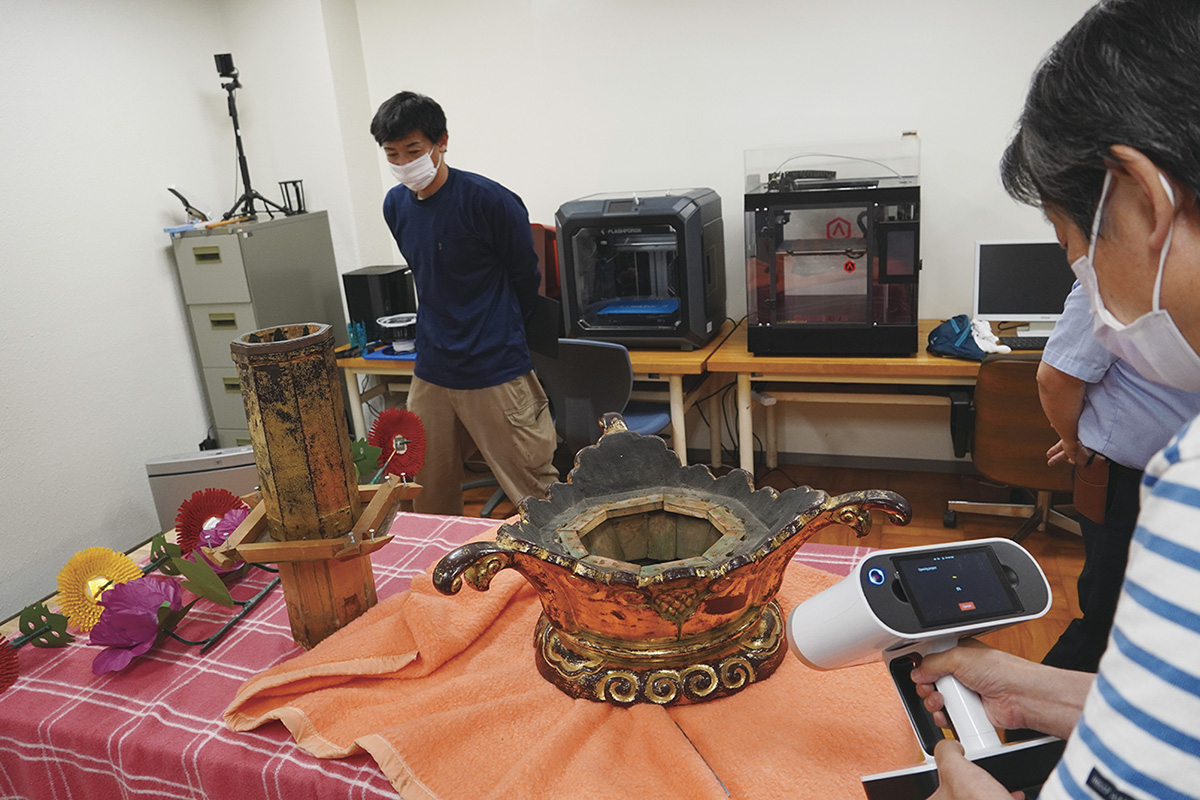

Survey on repair of Hokodome at Takaoka Mikurumayama Measurement using 3D scanner
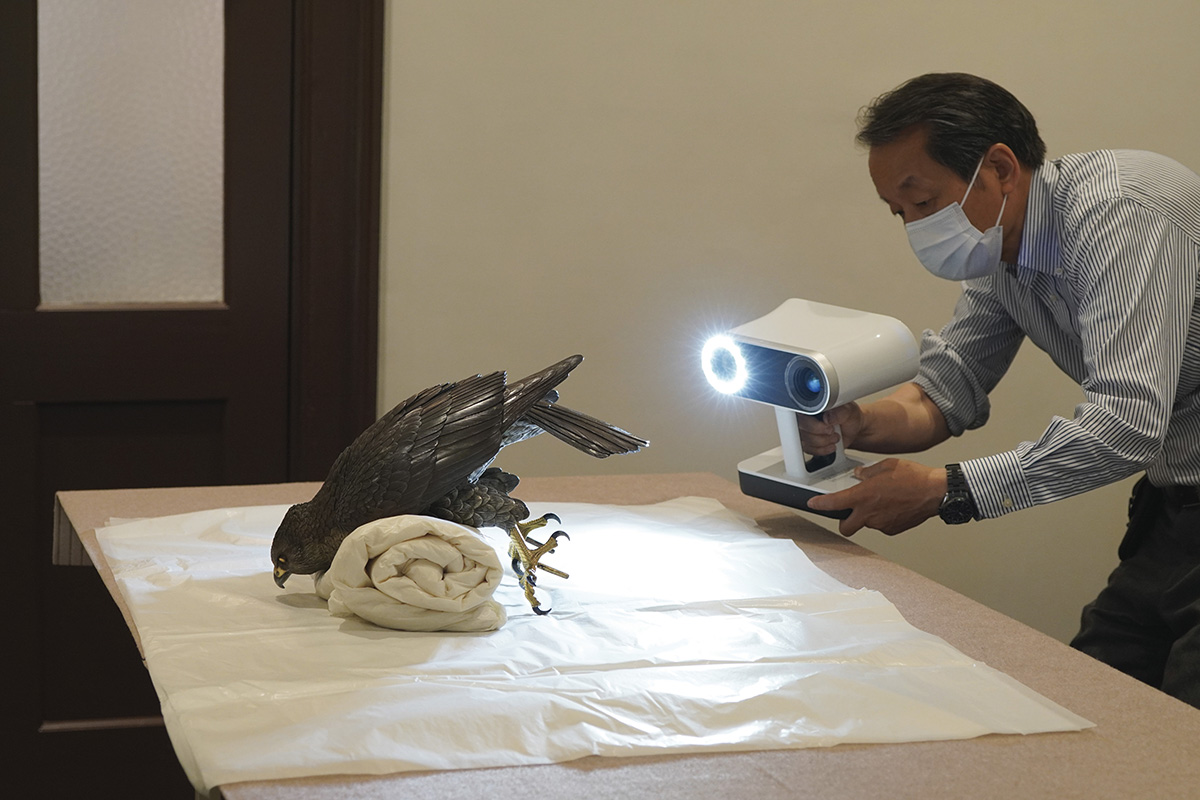

3D scanning for exhibition cooperation of the important cultural property “Twelve Eagles” from the National Museum of Arts and Crafts
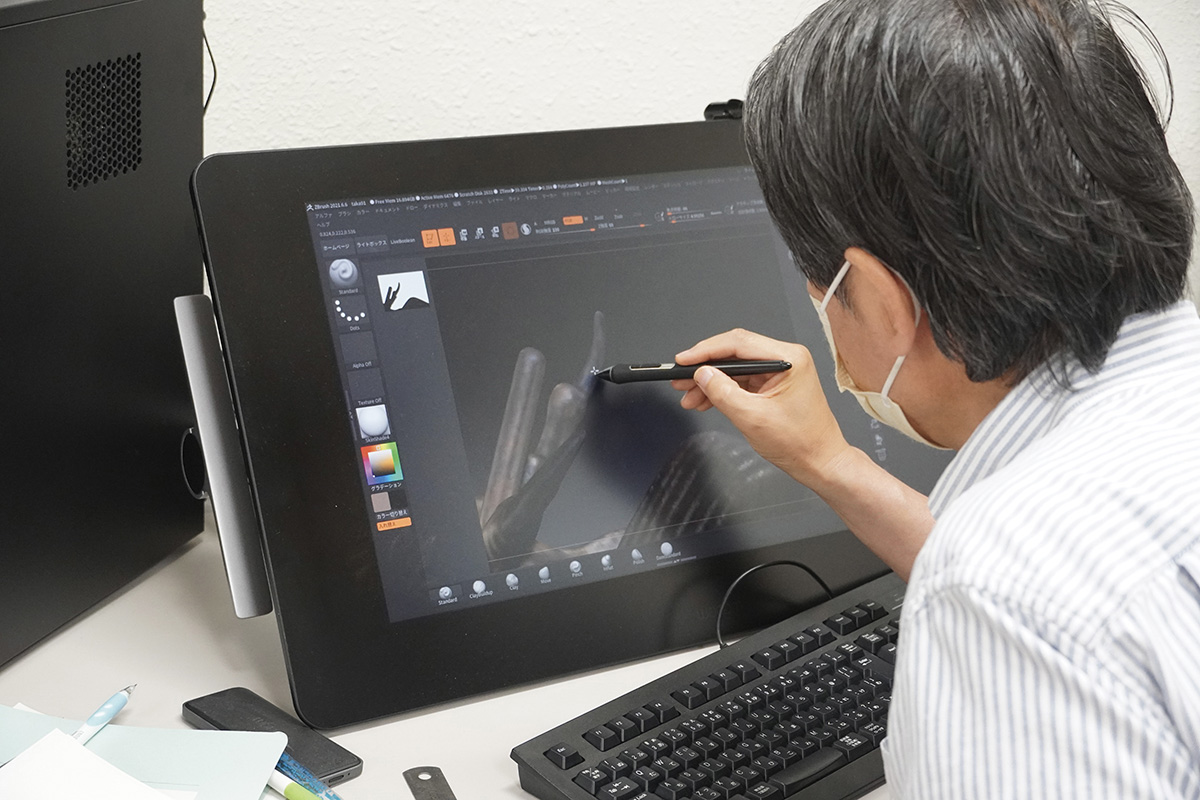

Data editing of the Crafts Museum “Twelve Eagles” using Zbrush
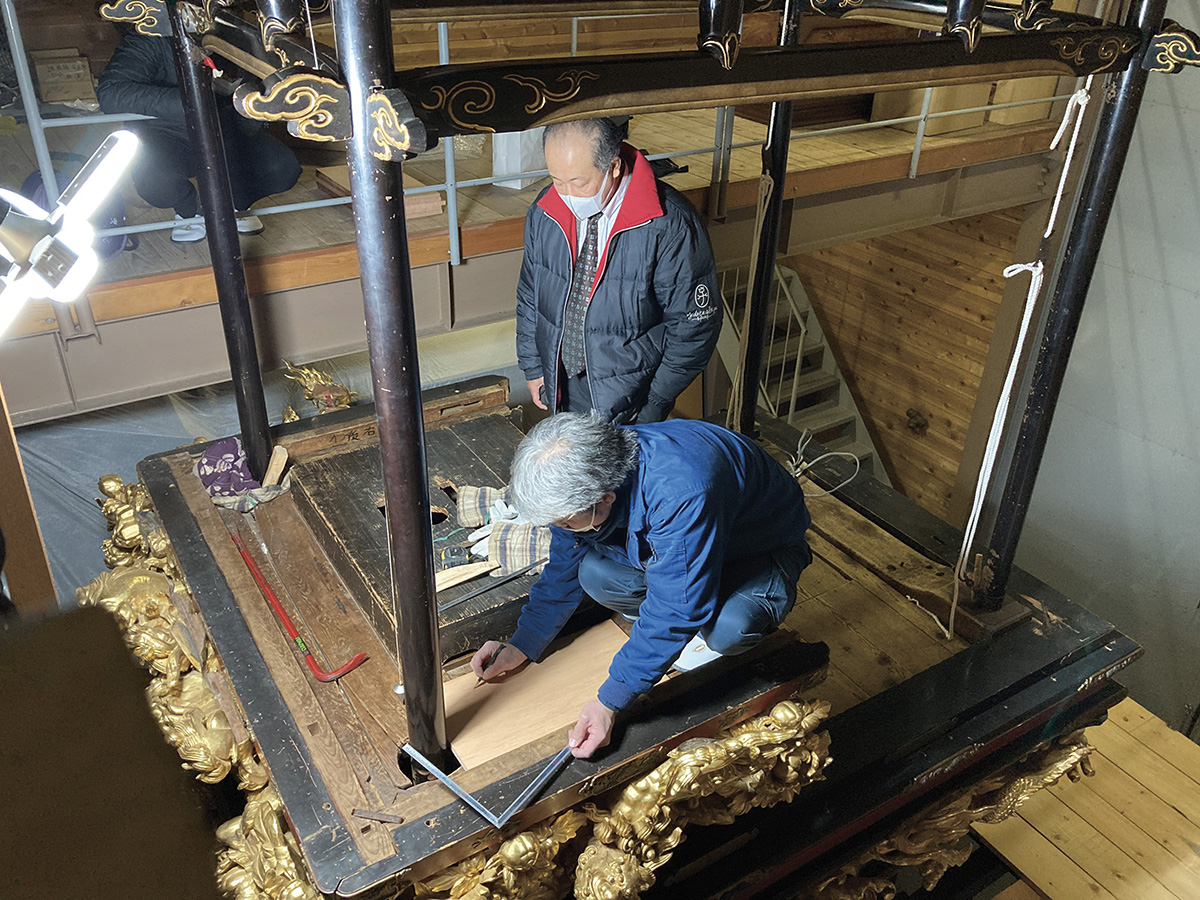

Measurement Survey for Repair of Four Pillars of Jyohana Hikiyama Festival Stalls
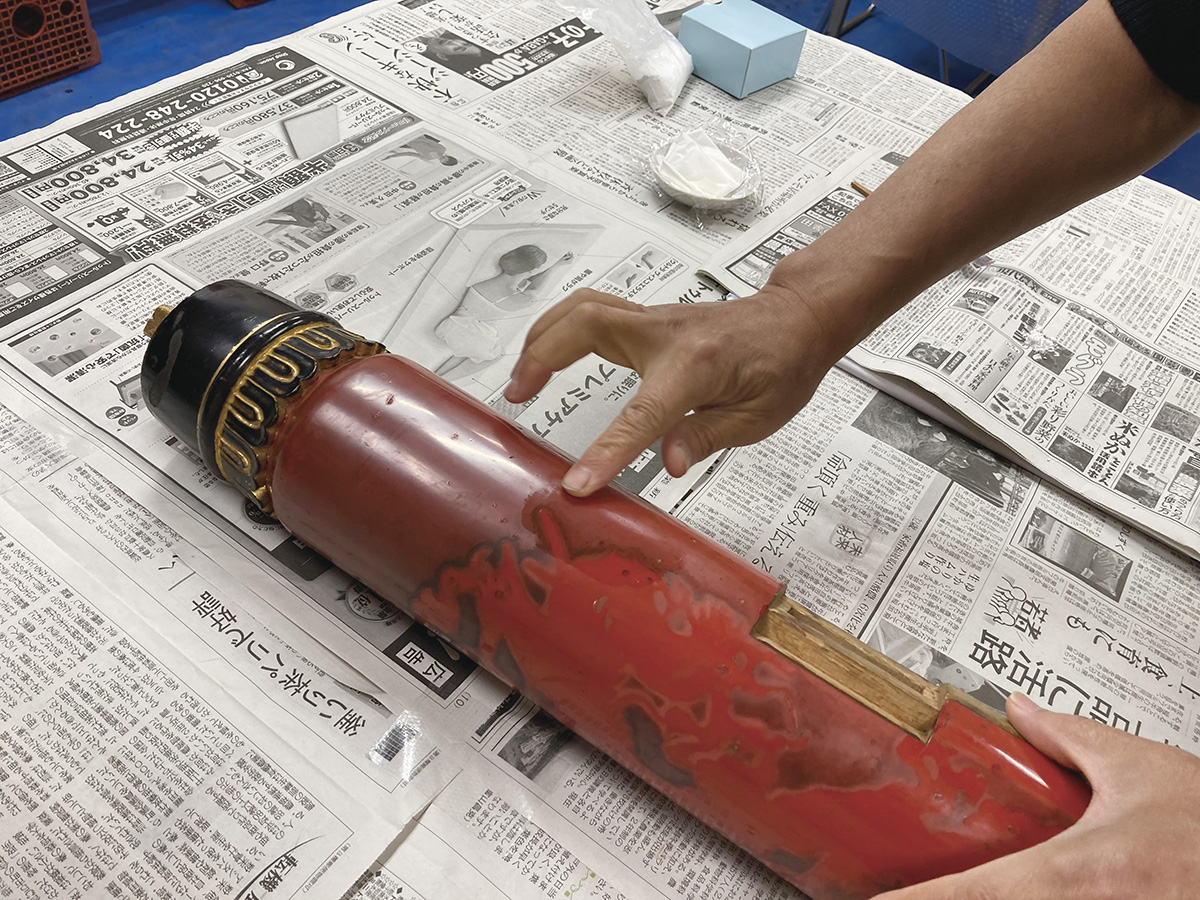

Survey of vermilion lacquer coating on the pillars of the Takaranbashira columns of the Shibata Hikiyama Festival stalls
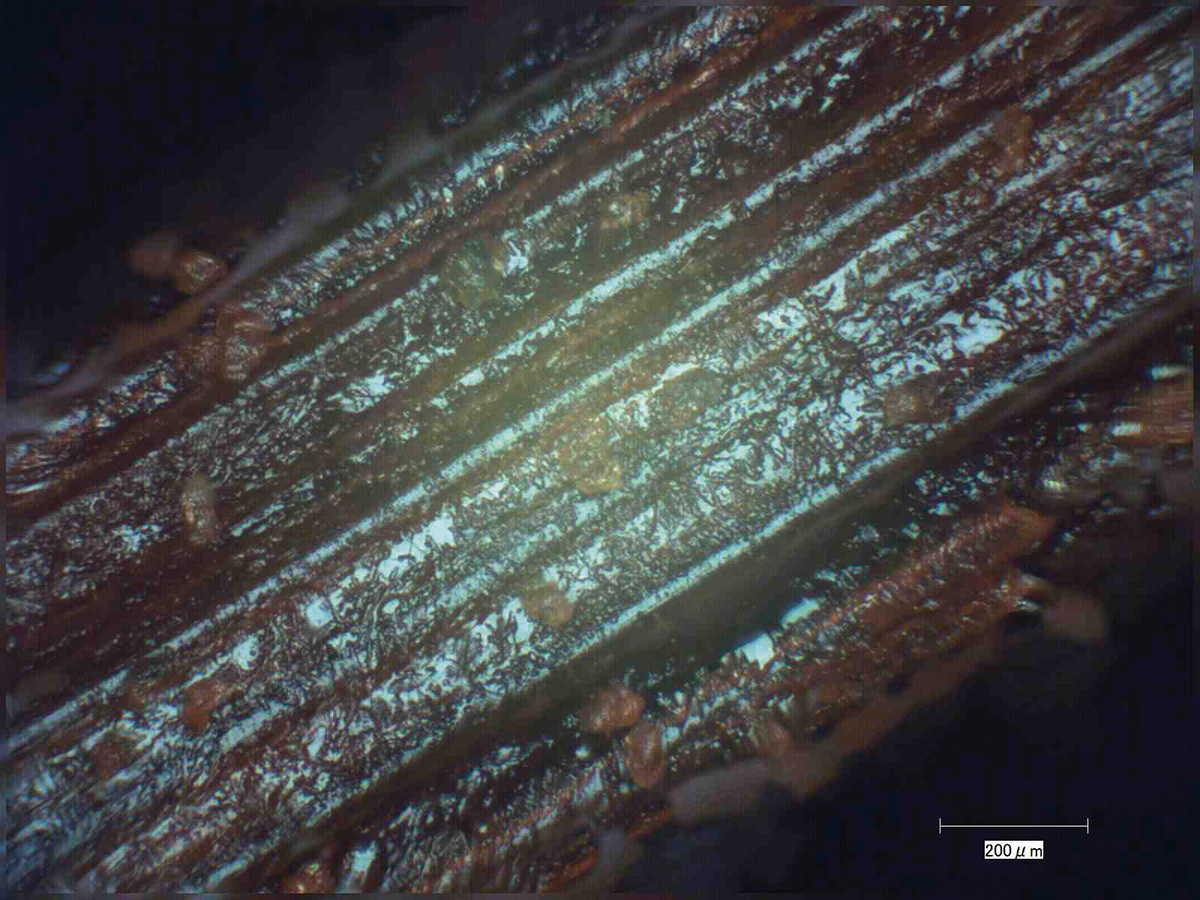

Enlarged image of a maki-e brush used by Gonroku Matsuda (Neji brush) before washing
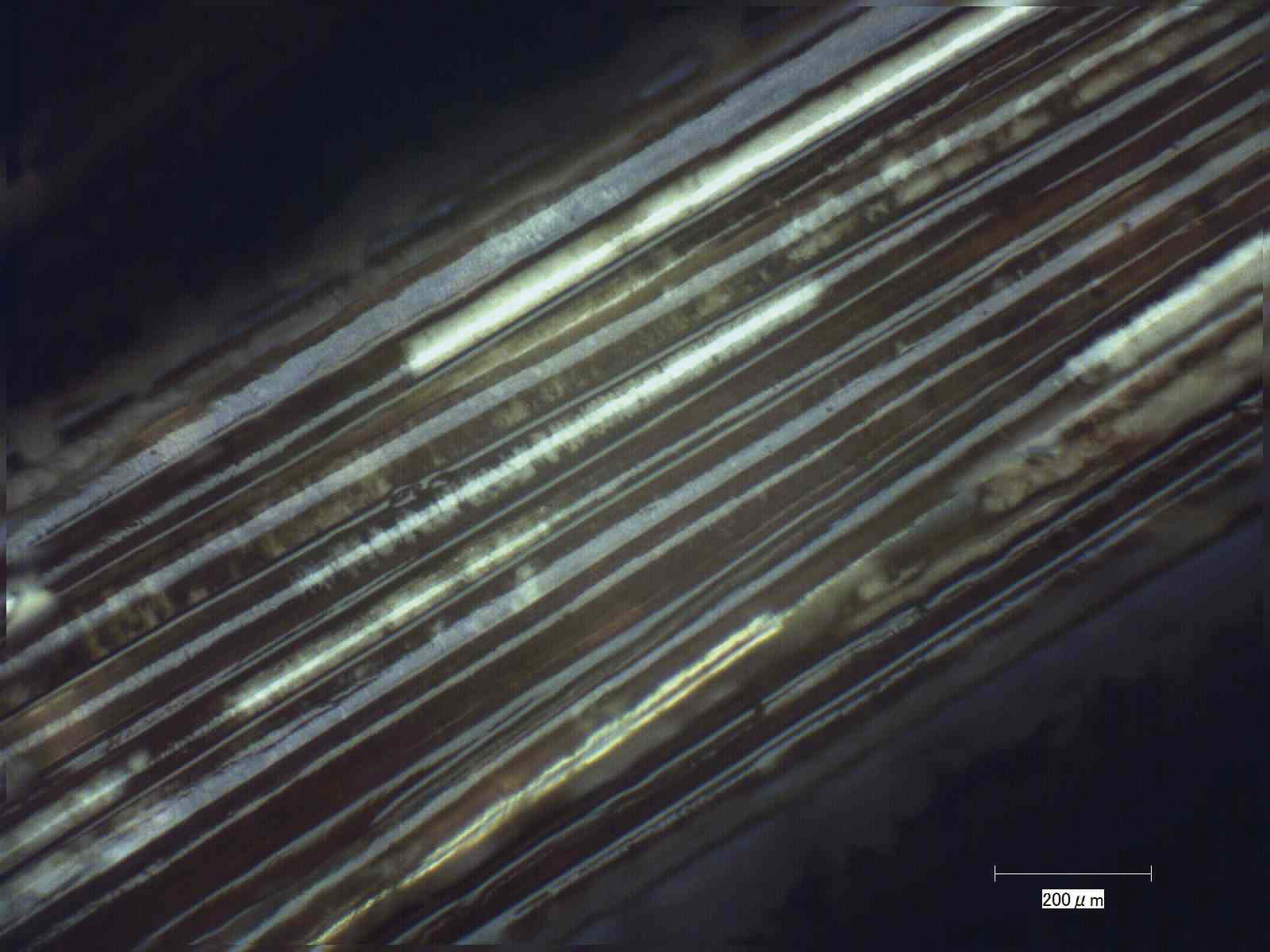

Enlarged image of a maki-e brush used by Gonroku Matsuda (Neji brush) after washing
Maki-e brush cleaning by Gonroku Matsuda Attached to brush scissors made by a 3D printer and vibrated with a motor to clean the brush.

3D scanning for repair of “Takaoka Mikurumayama Ichibangai Street Hokodome,” a nationally designated Important Tangible Folk Cultural Property
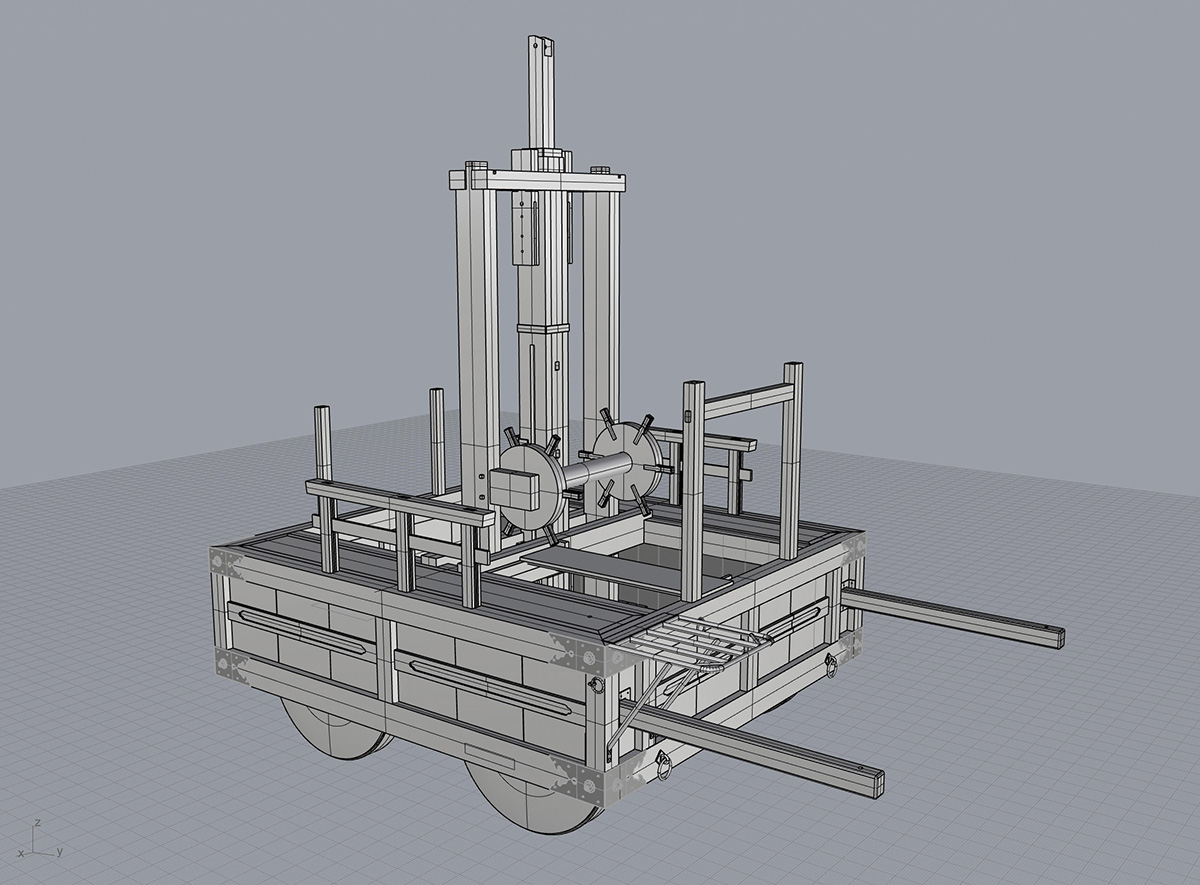
3D CAD data of the bogie section of the Karatsu-kunchi Ichiban “Red Lion"
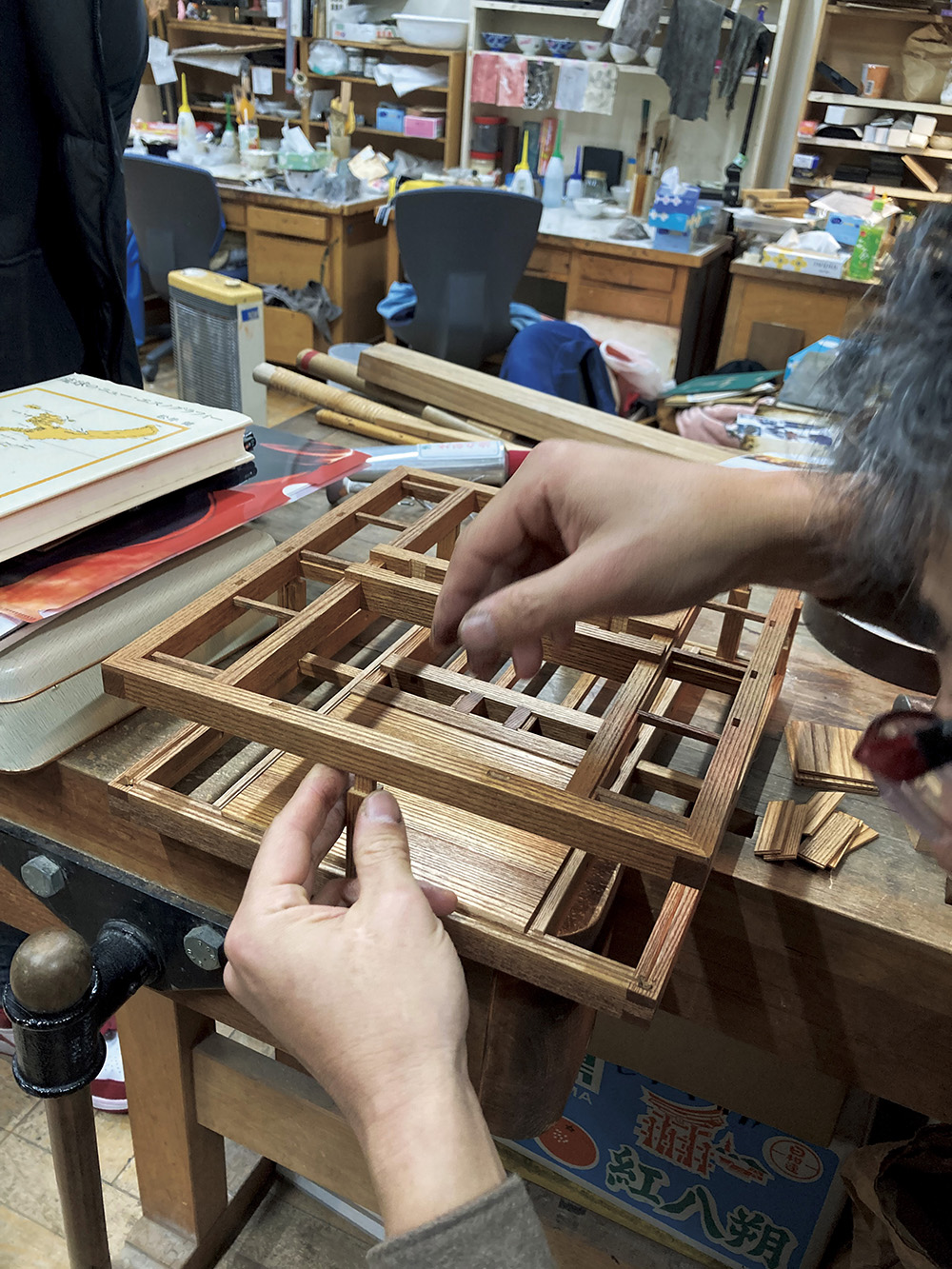

Karatsu-kunchi: 1/8th scale model of the “Akashishi” (red lion), the most popular float in Karatsu-kunchi. The cart is made by traditional woodwork technique.
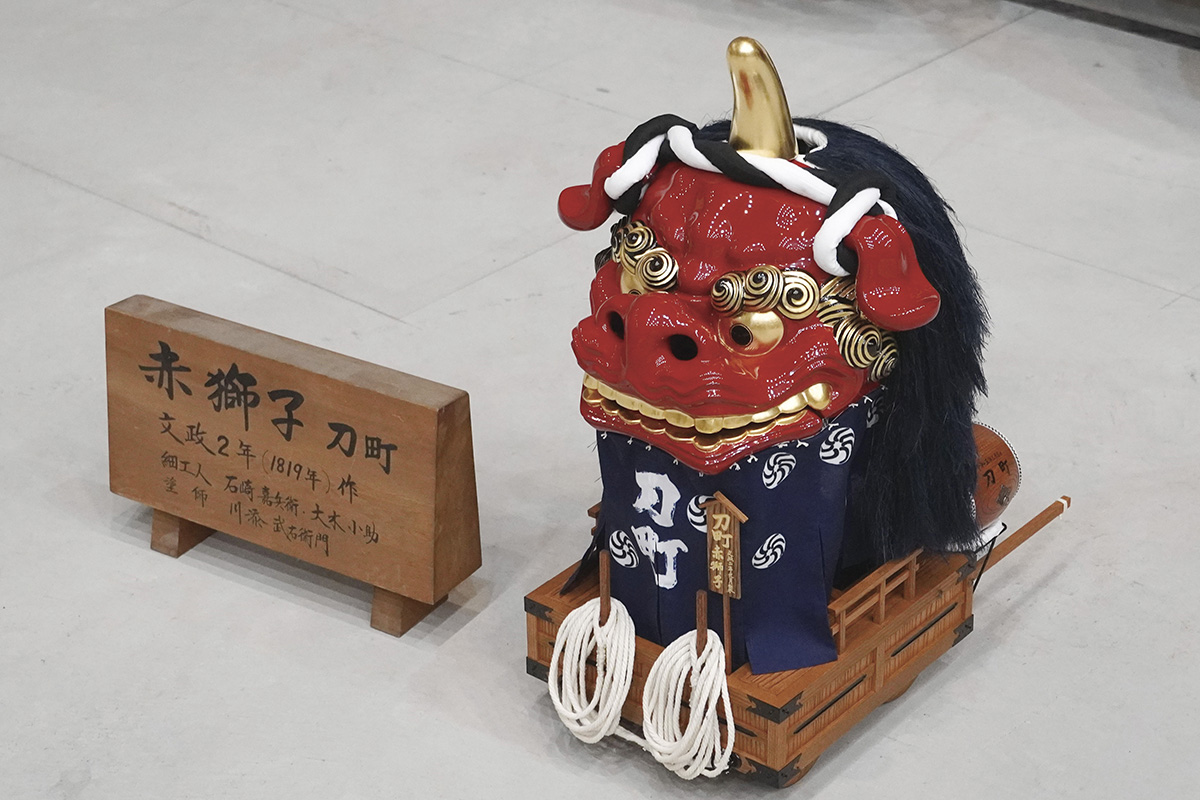

1/8th scale model of the “Akashishi” (red lion), the most popular floats of Karatsu-kunchi
Takaoka Mikurumayama Hokodome Ryutou Mapping
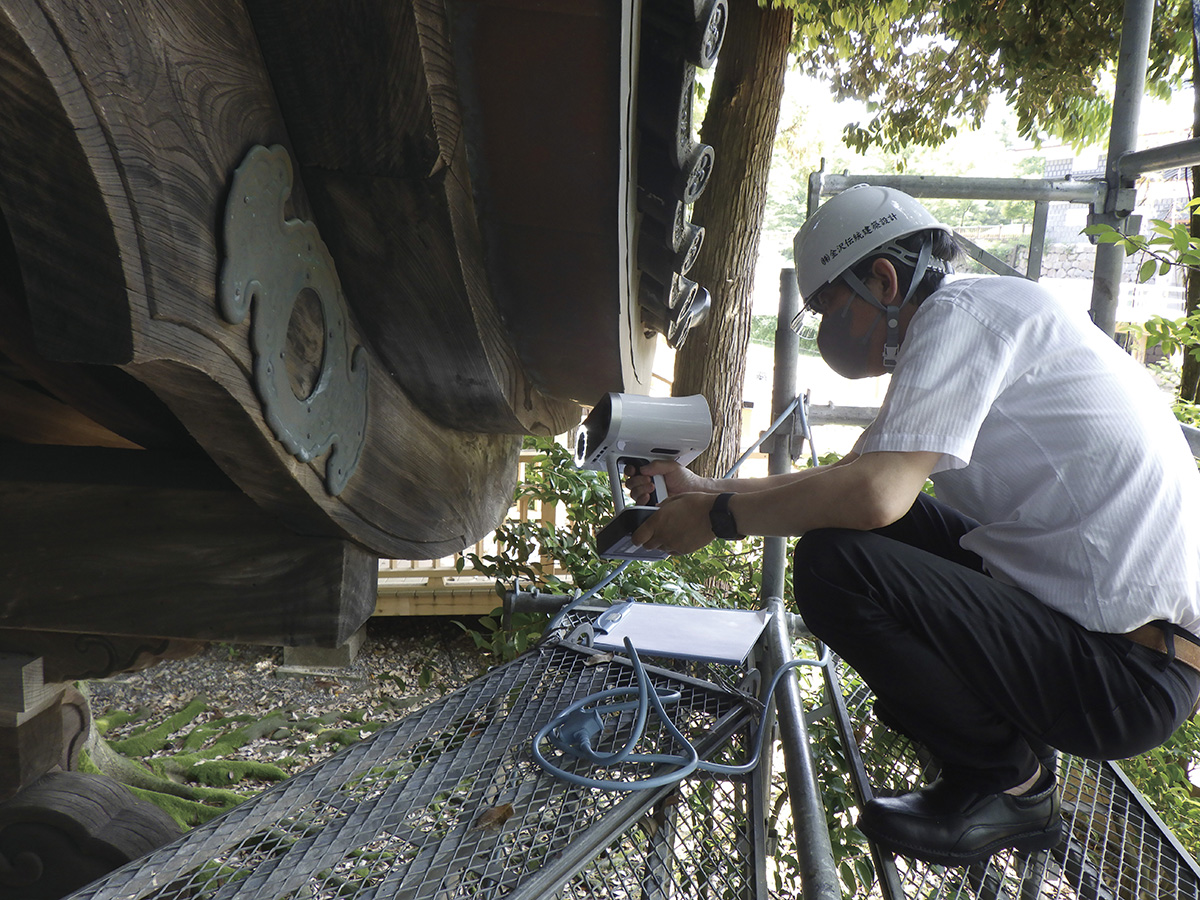

3D scanning of east gate metal fittings of Kanazawa Oyama Shrine
3D data of Oyama Shrine east shrine gate fittings
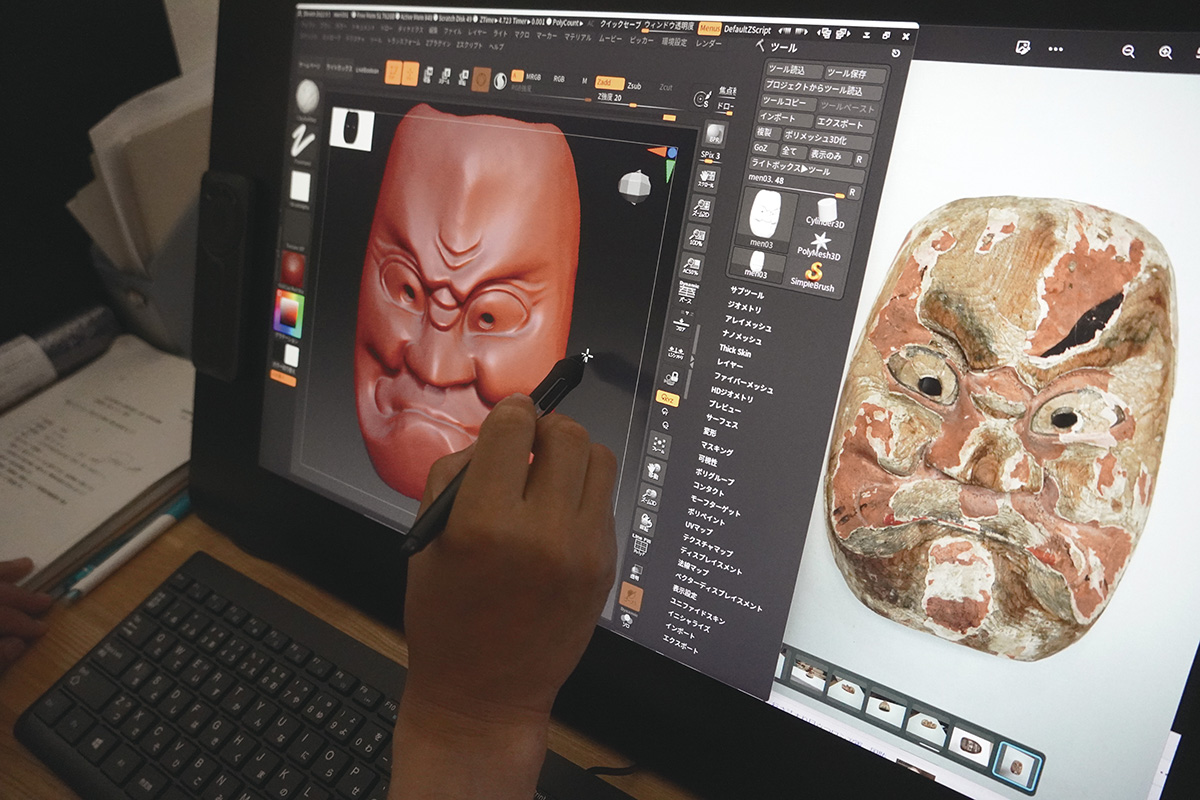

Futagami Imizu Shrine festival construction surface: using ZBrush to correct details in the scanned data.
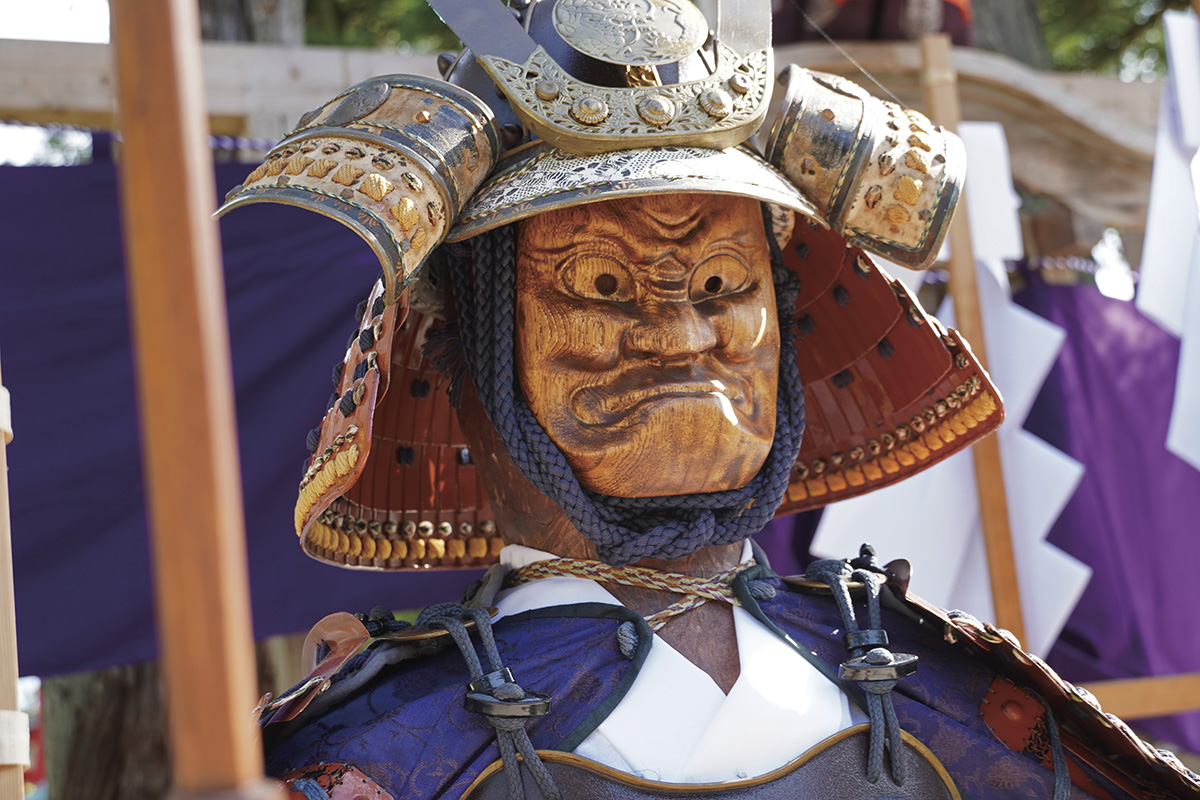

Reconstructed imitation masks used in the Futagami Imizu Shrine festival Tsukiyama event.
“Historical townscapes” exist in many parts of Japan. In Takaoka City (where GIGEIIN is located), there also exist historical townscapes such as “Kanayamachi” and “Yoshihisa” with their impressive “Samanoko” latticework, and “Yamacho-suji” with its rows of storehouse-style buildings. These are places where humans have lived and are an important tourist resource.
Tourism is one of the most important industries in Japan. Historical townscapes that can function as tourism resources should be protected and passed on.
What specific efforts are required to protect historical cityscapes and pass these on to future generations?
One of the typical elements of a historic townscape is “architecture”. Although “architecture” is a one-worded term, various structural types exist. Moreover, in certain areas, conventional wooden structures and
brick-and-reinforced-concrete structures can be observed in modern and post-modern architecture. To preserve the historical townscape that each region displays, it is essential to protect and pass on the architecture that exists there. Apparently, it is important to preserve the cultural elements of each historical townscape, such as its historical background, industry, and livelihood. However, it is also highly important to preserve the architecture that visually constitutes the townscape. In addition, architecture plays the role of a habitat that functions as the foundation of culture. We consider that “inheriting the architecture” is
the basis for “inheriting the culture”. However, it is in “inheriting the architecture” that the difficulty of historical townscape preservation lies.
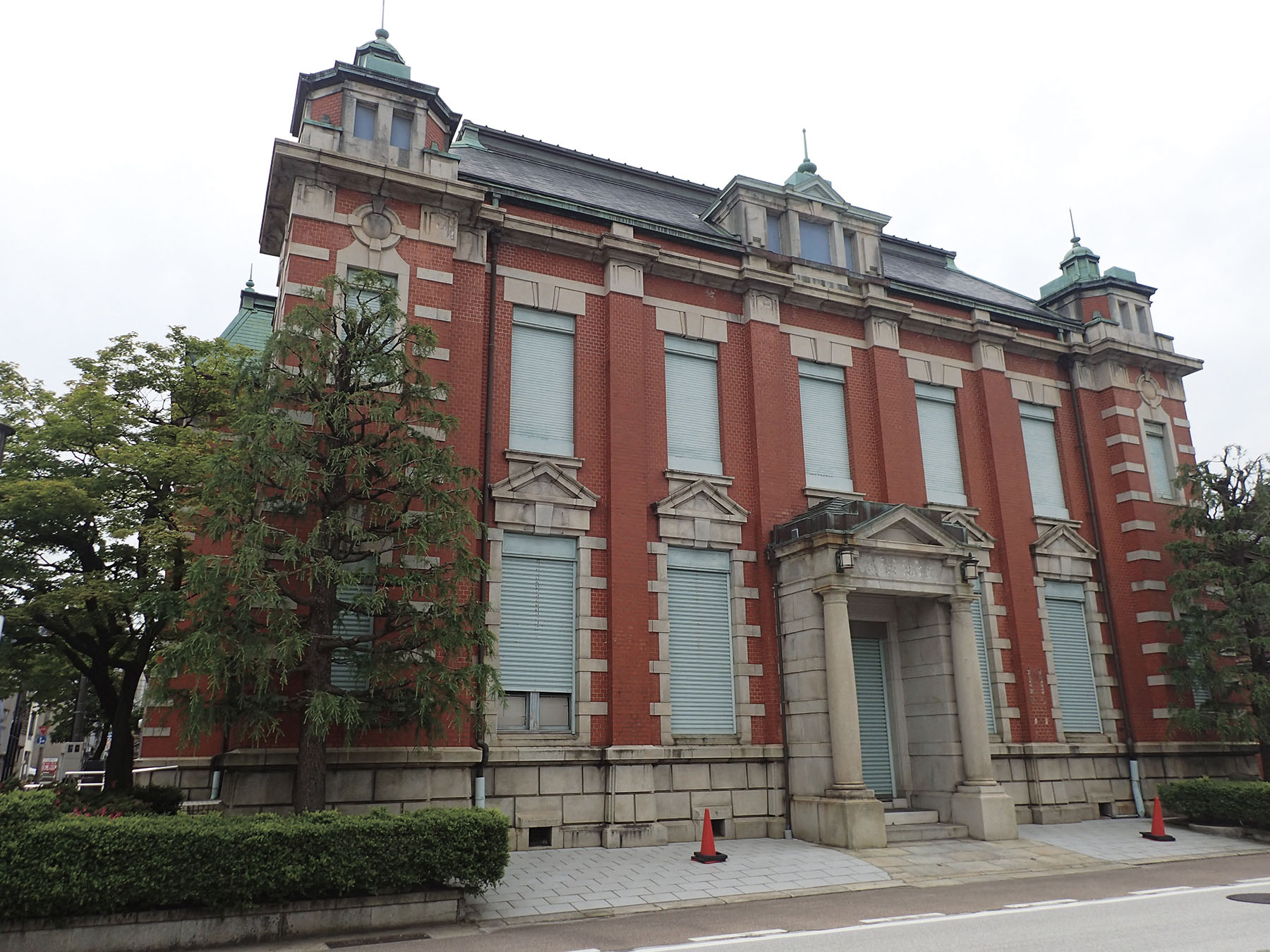

Former Toyama Bank Head Office
There are multiple challenges to architectural succession. First, there are issues related to the building strength,
such as aging and deficient seismic resistance owing to
the state of legislation at the time of construction.
Second, there are issues related to the cost of building maintenance. Third, the knowledge and guidelines for preserving historical buildings is insufficient. Although these issues may appear to be independent problems, these are deeply interrelated and increase the obstruction to the preservation of historical buildings.
However, without the inheritance of historical buildings,
the preservation of historical townscapes (which are
the assets of Japan and its residents) would be infeasible. Moreover, we cannot regain historical buildings and townscapes that have been lost. Thus, because many historical buildings still exist, we need to develop
an environment that enables the succession of historical buildings.
Against this background, the Architectural Culture Division would work toward developing technologies and constructing social systems to provide knowledge for
the inheritance of historical buildings. In particular,
we would actively use advanced equipment (one of
the strengths of GIGEIIN) to solve problems from
a completely new perspective.
The Noto Peninsula Earthquake of 2024 caused severe damage in Suzu, Wajima, and other areas in Hokuriku. Many individuals lost their living space owing to
the collapse of buildings caused by the violent shaking
and damage caused by liquefaction. As a research
institute in Hokuriku, we consider that we have
a responsibility to seriously consider what we can do
for those affected by the earthquake and what we should do for the region. The Group of Architectural and
Cultural of GIGEIIN intends to actively collaborate
in the reconstruction of the region.
Using a 3D scanner owned by GIGEIIN, we have started an initiative to record the shapes of existing historical buildings and other structures as point cloud data. Point cloud data is a collection of points with three-dimensional location and color information that records the shape of the object. Examples of point cloud data measured by the 3D scanner owned by GIGEIIN are shown in the photographs below. Photograph 1 displays the exterior of the previous Toyama Bank Head Office, and Photograph 2 displays the point cloud data of Fukuno Andon in Nanto City, Toyama Prefecture. The point cloud data can be incorporated into a VR space. Therefore, it is likely to be used for tourism promotion and regional revitalization.
In Nepal, many masonry buildings collapsed after the Gurkha earthquake in 2015. Since 2016, we have
been conducting on-site surveys and working with Tribhuvan University (Nepalʼs only national university) to improve masonry joints. In our research, we observed
that adding lime and rock salt to the local red clay,
as well as maintaining an appropriate moisture content,
increased the strength of the joints by approximately
three times. The results of this research were published as international papers in 2018 and 2023. The Kathmandu office of UNESCO and the Department of Archaeology
of the Government of Nepal are interested in the results
of the research. They have verbally agreed to
collaborate on the research on methods of restoration
of masonry buildings. During the course of this research, communication was interrupted for three years owing
to the global spread of COVID-19. However, in 2023,
the local meetings resumed, and discussions regarding
the 3D digital archiving of historical buildings (including World Heritage sites) are continuing using the new equipment and technology available with the Institute
of Technological Sciences.
The Nepalese government has imposed stringent regulations on the reconstruction of masonry buildings. This has hindered the use of conventional construction methods. However, we are preparing to construct a reinforced masonry community center in collaboration with the local Tribhuvan University and Kopa Institute
of Technology.
There are no articles to display.
